Remotely sensed crown nutrient concentrations modulate forest reproduction across the contiguous United States
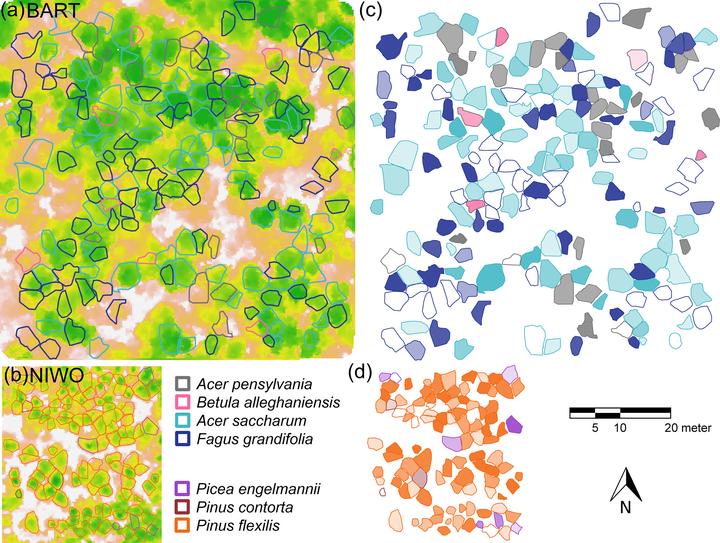 Crown delineation in a deciduous-dominant large plot at Bartlett Experimental Forest (BART, panel a) and a conifers-dominant small plot at Niwot Ridge (NIWO, panel b). The canopy height model is shown in the background, where green means a high value and brown indicates a low value. Mature individuals with fecundity estimates are colored by their species. Fecundity at each tree crown is summarized in panels (c) and (d), where higher transparency indicates low fecundity and vice versa. .
Crown delineation in a deciduous-dominant large plot at Bartlett Experimental Forest (BART, panel a) and a conifers-dominant small plot at Niwot Ridge (NIWO, panel b). The canopy height model is shown in the background, where green means a high value and brown indicates a low value. Mature individuals with fecundity estimates are colored by their species. Fecundity at each tree crown is summarized in panels (c) and (d), where higher transparency indicates low fecundity and vice versa. .
Abstract
Global forests are increasingly lost to climate change, disturbance, and human management. Evaluating forests' capacities to regenerate and colonize new habitats has to start with the seed production of individual trees and how it depends on nutrient access. Studies on the linkage between reproduction and foliar nutrients are limited to a few locations and few species, due to the large investment needed for field measurements on both variables. We synthesized tree fecundity estimates from the Masting Inference and Forecasting (MASTIF) network with foliar nutrient concentrations from hyperspectral remote sensing at the National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON) across the contiguous United States. We evaluated the relationships between seed production and foliar nutrients for 56,544 tree-years from 26 species at individual and community scales. We found a prevalent association between high foliar phosphorous (P) concentration and low individual seed production (ISP) across the continent. Within-species coefficients to nitrogen (N), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg) are related to species differences in nutrient demand, with distinct biogeographic patterns. Community seed production (CSP) decreased four orders of magnitude from the lowest to the highest foliar P. This first continental-scale study sheds light on the relationship between seed production and foliar nutrients, highlighting the potential of using combined Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) and hyperspectral remote sensing to evaluate forest regeneration. The fact that both ISP and CSP decline in the presence of high foliar P levels has immediate application in improving forest demographic and regeneration models by providing more realistic nutrient effects at multiple scales.